Tinnitus affects roughly 15% of American adults, creating a constant ringing or buzzing that disrupts daily life and sleep. At NuMed DPC, we recognize that conventional treatments don’t work for everyone, which is why exploring natural therapy for tinnitus relief has become increasingly important.
Many patients find that addressing root causes like inflammation, stress, and nutritional deficiencies offers real relief without relying solely on medications. This guide walks you through evidence-based natural approaches that can meaningfully reduce your symptoms.
Understanding Tinnitus: What It Is and Why It Happens
Tinnitus is the perception of sound without an external source, and about 27 million Americans experience it according to the American Tinnitus Association. The condition manifests as ringing, buzzing, hissing, or roaring in one or both ears, and severity varies dramatically from person to person. Some people notice it only in quiet environments at night, while others hear it constantly throughout their day, affecting concentration, sleep quality, and emotional well-being. The key distinction is that tinnitus itself is not a disease but a symptom pointing to underlying dysfunction in how your auditory system and brain process sound signals.
Hearing Loss and Inflammation as Primary Drivers
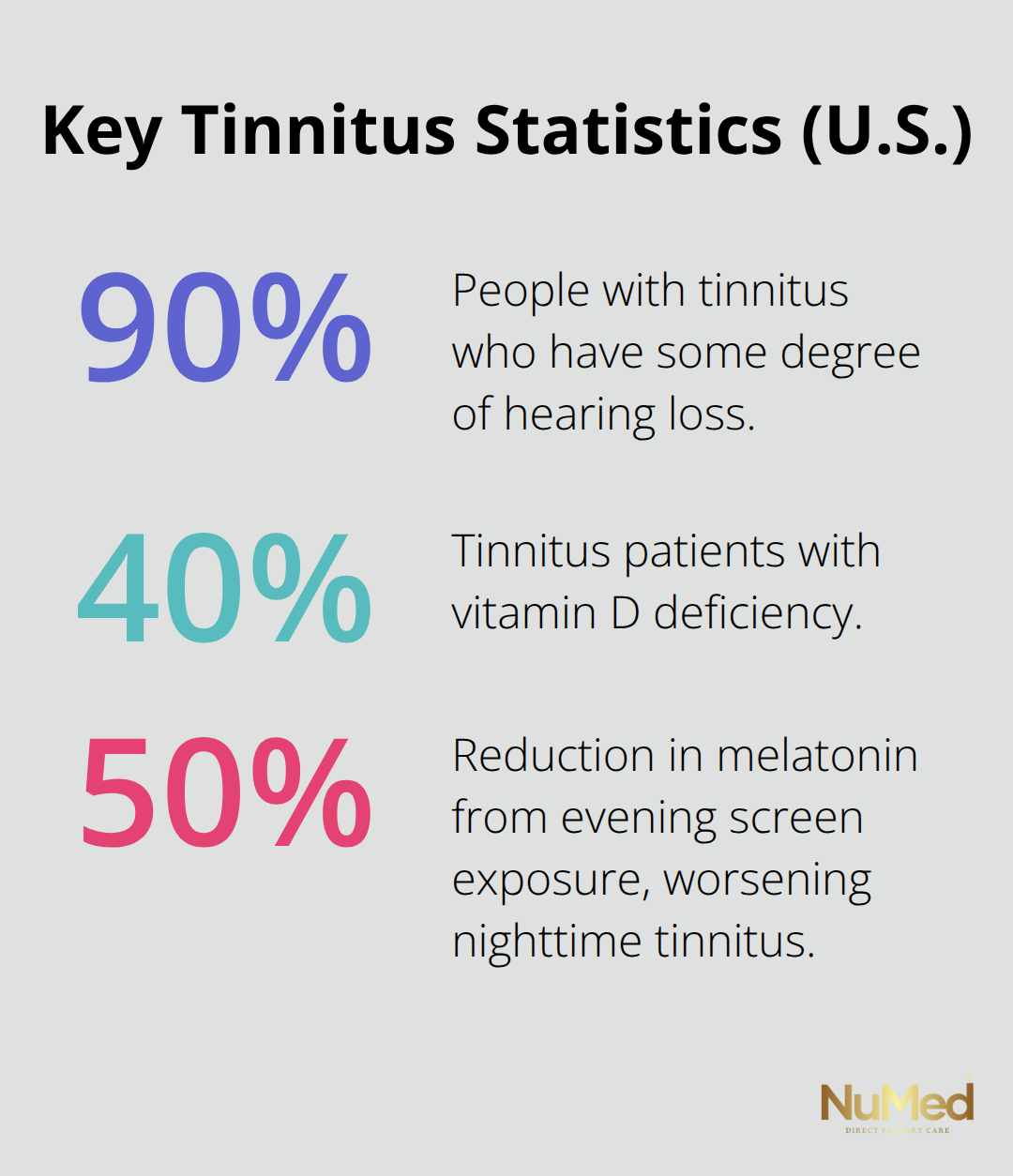
Roughly 90 percent of people with tinnitus have some degree of hearing loss. Beyond hearing loss, inflammation in the inner ear, auditory nerve, or brain’s auditory processing centers frequently triggers or worsens tinnitus symptoms. Chronic inflammation reduces blood flow to sensitive auditory structures and disrupts the delicate balance of neurotransmitters that regulate sound perception.
Stress amplifies this inflammatory response through your fight-or-flight system, which constricts blood vessels and increases cortisol production. Nutritional deficiencies in magnesium, zinc, vitamin B12, and vitamin D also contribute significantly to tinnitus severity, as these nutrients support nerve function and reduce oxidative stress in auditory tissues.
The Limitations of Conventional Medical Treatment
Conventional medicine typically addresses tinnitus with medications like gabapentin or antidepressants, yet these drugs provide minimal relief for most patients and carry side effects that worsen quality of life. Hearing aids help some people (they amplify external sounds and mask the internal tinnitus), but they do not address the root inflammatory or nutritional causes driving the condition. Surgery rarely offers a solution since tinnitus rarely stems from a surgically correctable problem.
The fundamental limitation of conventional approaches is that they treat tinnitus as an isolated symptom rather than a signal that your body needs systemic support. Medications and devices miss the opportunity to address inflammation, nutritional status, stress levels, and sleep quality-the factors that actually control how loudly your brain perceives tinnitus. This is where natural therapy approaches offer a different path forward, one that targets the mechanisms underlying your symptoms rather than just masking them temporarily.
What Natural Methods Actually Work for Tinnitus
Sound Masking Reduces Tinnitus Awareness Immediately
Sound masking works by introducing external noise at low volumes, which shifts your brain’s attention away from the tinnitus signal rather than amplifying silence that makes internal sounds louder. White noise machines, fans, nature sound apps, or soft background music during work hours create an acoustic environment that reduces tinnitus awareness without requiring active effort. A 2020 study found that personalized sound selection, choosing frequencies and tones that match your specific tinnitus pitch, produces better outcomes than generic white noise. Test different sound types for one to two weeks each, noting which reduces your perception most effectively. If you have concurrent hearing loss, hearing aids with built-in masking features serve double duty by amplifying external sounds while simultaneously providing tinnitus relief through the same masking mechanism.
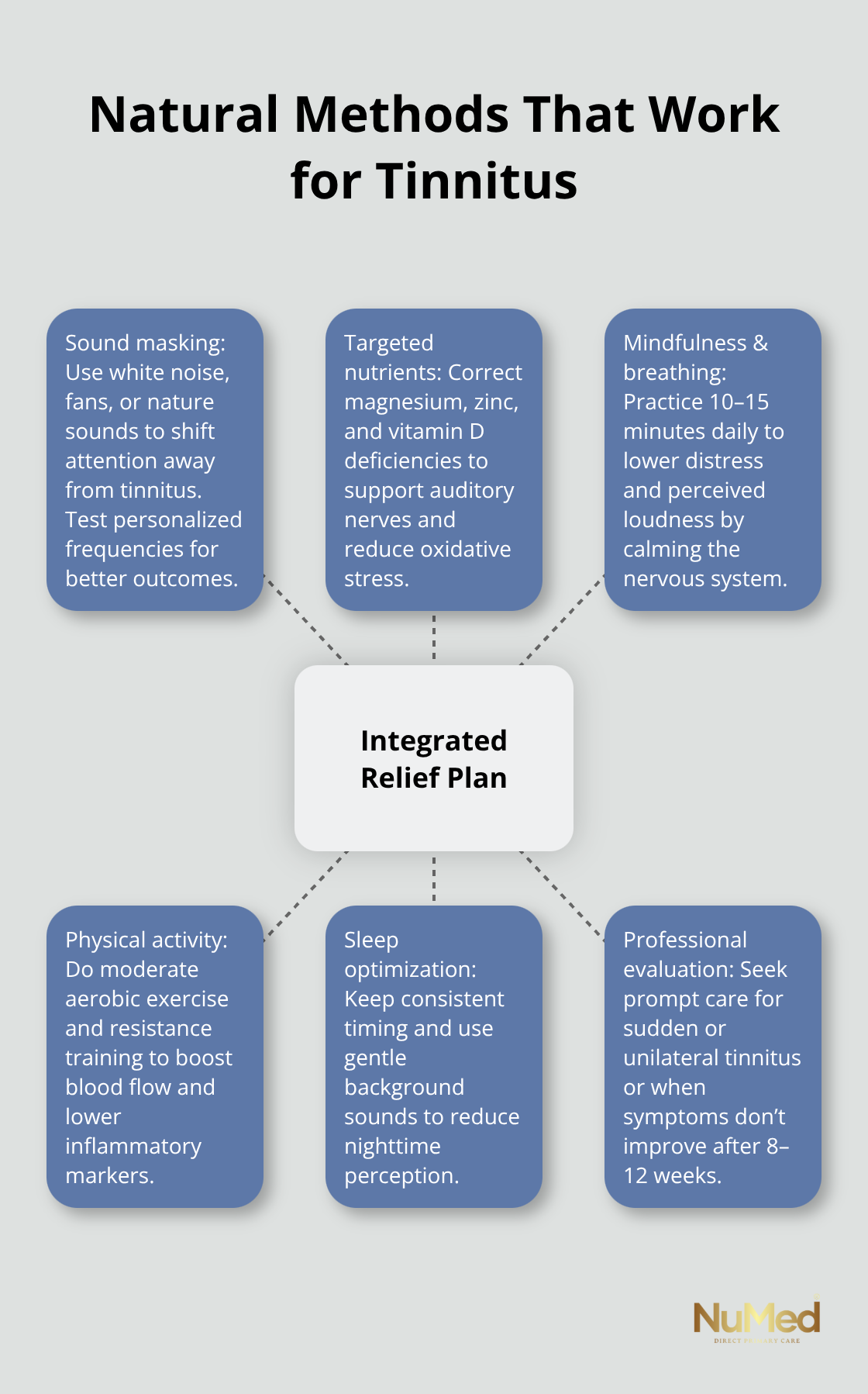
Magnesium and Zinc Address Core Nutritional Gaps
Magnesium deficiency stands out as one of the strongest nutritional links to tinnitus severity because this mineral regulates nerve signaling in auditory tissues. Most adults consume only 40 to 50 percent of the recommended daily intake, making supplementation worthwhile. Typical dosing ranges from 300 to 500 mg daily, though absorption varies by form; magnesium glycinate and magnesium threonate cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively than oxide forms. Magnesium improves blood flow to the auditory system and helps reduce oxidative stress, making it a valuable supplement for ear function and tinnitus prevention. Zinc deficiency similarly correlates with tinnitus, particularly in older adults, and correcting documented deficiency through 25 to 30 mg daily can reduce symptom severity within 4 to 12 weeks. Vitamin D deficiency appears in roughly 40 percent of tinnitus patients, and correcting levels to 40 to 60 ng/mL has shown symptom improvement in clinical observation. Work with a clinician to identify which specific deficiencies apply to your situation before starting supplementation, rather than assuming you need all nutrients equally.
Vitamin B12 and Auditory Nerve Function
Vitamin B12 supports auditory nerve function, though supplementation helps those with documented deficiency more than people with normal B12 levels. Randomized trials show limited benefit for individuals without a deficiency, making testing your actual status the first step. If your clinician confirms low B12, supplementation can contribute to your overall tinnitus management plan alongside other interventions.
Mindfulness and Breathing Techniques Lower Perceived Loudness
Stress amplifies tinnitus perception through cortisol elevation and blood vessel constriction, making stress management foundational rather than optional. Mindfulness-based interventions show particularly strong evidence; a 2019 systematic review found that 6 of 7 studies demonstrated clinically meaningful tinnitus distress reduction with mindfulness practice. The practical protocol involves 10 to 15 minutes of daily practice, focusing on observing tinnitus sensations without judgment rather than fighting them. Deep breathing exercises-inhaling for a count of four, holding for four, exhaling for six-activate your parasympathetic nervous system and demonstrably lower perceived tinnitus loudness within minutes.
Physical Activity and Sleep Quality: Complete the Foundation
Physical activity improves blood flow to auditory structures and reduces cortisol; even 30 minutes of moderate activity three times weekly correlates with symptom improvement. Sleep quality directly influences tinnitus severity because poor sleep amplifies your brain’s sensitivity to internal sounds. Maintain consistent sleep timing, avoid screens one hour before bed, and use gentle background sounds to create the sleep environment that allows your nervous system to recover. These lifestyle modifications work synergistically, combining sound masking with nutritional correction and stress reduction produces substantially better outcomes than any single approach alone. The next step involves identifying which of these natural methods addresses your specific tinnitus triggers, which requires understanding your individual symptom patterns and underlying causes.
Building Your Anti-Inflammatory Tinnitus Plan
Inflammation in auditory tissues drives tinnitus severity more directly than most patients realize, which means your dietary and exercise choices become medical interventions rather than general wellness habits. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids may help preserve auditory function; fatty fish like salmon and sardines contain omega-3 compounds that support auditory health. Leafy greens, berries, and whole grains contain polyphenols that cross the blood-brain barrier and reduce oxidative stress in auditory processing centers. Conversely, seed oils high in omega-6 linoleic acid, refined carbohydrates, and processed foods amplify systemic inflammation within weeks of consistent consumption. Most tinnitus patients see measurable symptom reduction within 4 to 8 weeks of shifting to a Mediterranean-style diet, which emphasizes fish, olive oil, vegetables, and legumes while eliminating ultra-processed foods.
Exercise Reduces Inflammatory Markers Directly
Exercise acts as a systemic anti-inflammatory agent; moderate aerobic activity, 150 minutes weekly, increases blood flow to the cochlea and auditory nerve while lowering cortisol and TNF-alpha levels documented in tinnitus research. Resistance training twice weekly provides additional benefit by improving metabolic control and reducing inflammatory markers further. The critical detail most clinicians miss is timing: consuming anti-inflammatory foods immediately after exercise amplifies nutrient absorption and recovery signaling, making post-workout meals your highest-leverage nutritional window.
Sleep Architecture Controls Tinnitus Perception
Sleep disturbance affects 50–75% of patients with chronic tinnitus and has been identified as a possible cause of tinnitus. Your brain’s auditory filtering system requires deep sleep to consolidate sound processing and reduce sensitivity to repetitive signals. Consistent sleep timing matters more than total hours; maintaining the same bedtime and wake time within 30 minutes daily stabilizes circadian regulation of auditory processing. Environmental darkness triggers melatonin production, which reduces inflammation and supports mitochondrial function in auditory tissues; exposure to screens within two hours of bedtime suppresses melatonin by 50 percent and directly worsens nighttime tinnitus. White noise or nature sounds at 50 to 60 decibels mask tinnitus during the sleep onset phase when your brain is most sensitive to internal sounds.

Magnesium supplementation taken 30 to 60 minutes before bed improves sleep quality while simultaneously supporting auditory nerve function through the same mechanism. Avoid alcohol and caffeine after 2 PM to prevent sleep fragmentation that amplifies tinnitus during lighter sleep stages. The combination of consistent timing, environmental masking, and magnesium supplementation produces better sleep outcomes than any single intervention, which then reduces daytime tinnitus perception substantially.
Professional Evaluation Identifies Treatable Conditions
Sudden tinnitus onset, unilateral symptoms affecting only one ear, or tinnitus accompanied by dizziness, ear pain, or progressive hearing loss requires immediate professional evaluation because these patterns indicate treatable underlying conditions like sudden sensorineural hearing loss, TMJ dysfunction, or middle ear fluid accumulation. A comprehensive hearing evaluation identifies whether concurrent hearing loss exists, which changes your treatment strategy significantly since hearing aids with masking features address both conditions simultaneously. If natural approaches show no improvement after 8 to 12 weeks of consistent implementation, professional guidance helps identify whether somatic tinnitus stemming from neck tension or jaw dysfunction requires physical therapy, or whether emerging therapies like bimodal neuromodulation warrant consideration. Your clinician can also screen for medication side effects causing tinnitus; certain blood pressure medications, antibiotics, and chemotherapy agents trigger or worsen symptoms, making medication review essential before assuming your tinnitus requires new treatment.
Final Thoughts
Natural therapy for tinnitus works because it targets the mechanisms driving your symptoms rather than masking them temporarily. Sound masking, nutritional correction, stress reduction, anti-inflammatory diet, exercise, and sleep optimization form an integrated system where each component strengthens the others. Magnesium and zinc address documented deficiencies that amplify auditory nerve dysfunction, while mindfulness and breathing techniques lower perceived loudness by calming your nervous system. Physical activity and consistent sleep timing reduce inflammation and restore your brain’s ability to filter internal sounds effectively.
Identifying your personal tinnitus triggers separates effective treatment from wasted effort. Sudden onset, unilateral symptoms, or tinnitus accompanied by dizziness or hearing loss signal treatable underlying conditions requiring professional evaluation. Gradual onset linked to stress, poor sleep, or dietary patterns responds well to natural approaches implemented consistently over 8 to 12 weeks, with some patients seeing dramatic improvement from sound masking combined with magnesium supplementation, while others benefit most from sleep optimization and stress reduction alone.
Tinnitus management requires identifying your specific root causes and building a personalized plan rather than following generic protocols. We work with you to determine which nutritional deficiencies, inflammatory patterns, and lifestyle factors drive your tinnitus, then implement natural therapy for tinnitus systematically while monitoring your progress. If you are ready to address tinnitus through evidence-based natural approaches rather than accepting it as permanent, contact NuMed DPC to build your personalized relief plan.
















