Stress is a universal experience that affects everyone, but its impact on our lives is often underestimated. At NuMed DPC, we’ve seen firsthand how the principle of stress can significantly influence both physical and mental well-being.
Understanding this principle is crucial for managing our health and improving our quality of life. In this post, we’ll explore how stress affects your body and mind, and why it’s essential to develop effective coping strategies.
What Is Stress and How Does It Affect Us?
The Nature of Stress
Stress extends beyond feelings of overwhelm or anxiety. It represents a complex physiological response that impacts our entire body. At its essence, stress is our body’s reaction to any demand or challenge. Both positive and negative experiences can trigger this response, ranging from a job promotion to a family crisis.
The Stress Response: Fight, Flight, or Freeze
When we face a stressor, our body immediately shifts into high gear. The hypothalamus (a small region at the base of our brain) activates an alarm system in our body. This activation releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which prepare us for action.
This stress response, often termed “fight, flight, or freeze,” evolved to help us survive immediate physical dangers. However, in today’s world, we often confront ongoing stressors that maintain our body in a constant state of alertness. This persistent state can lead to a range of health problems over time.
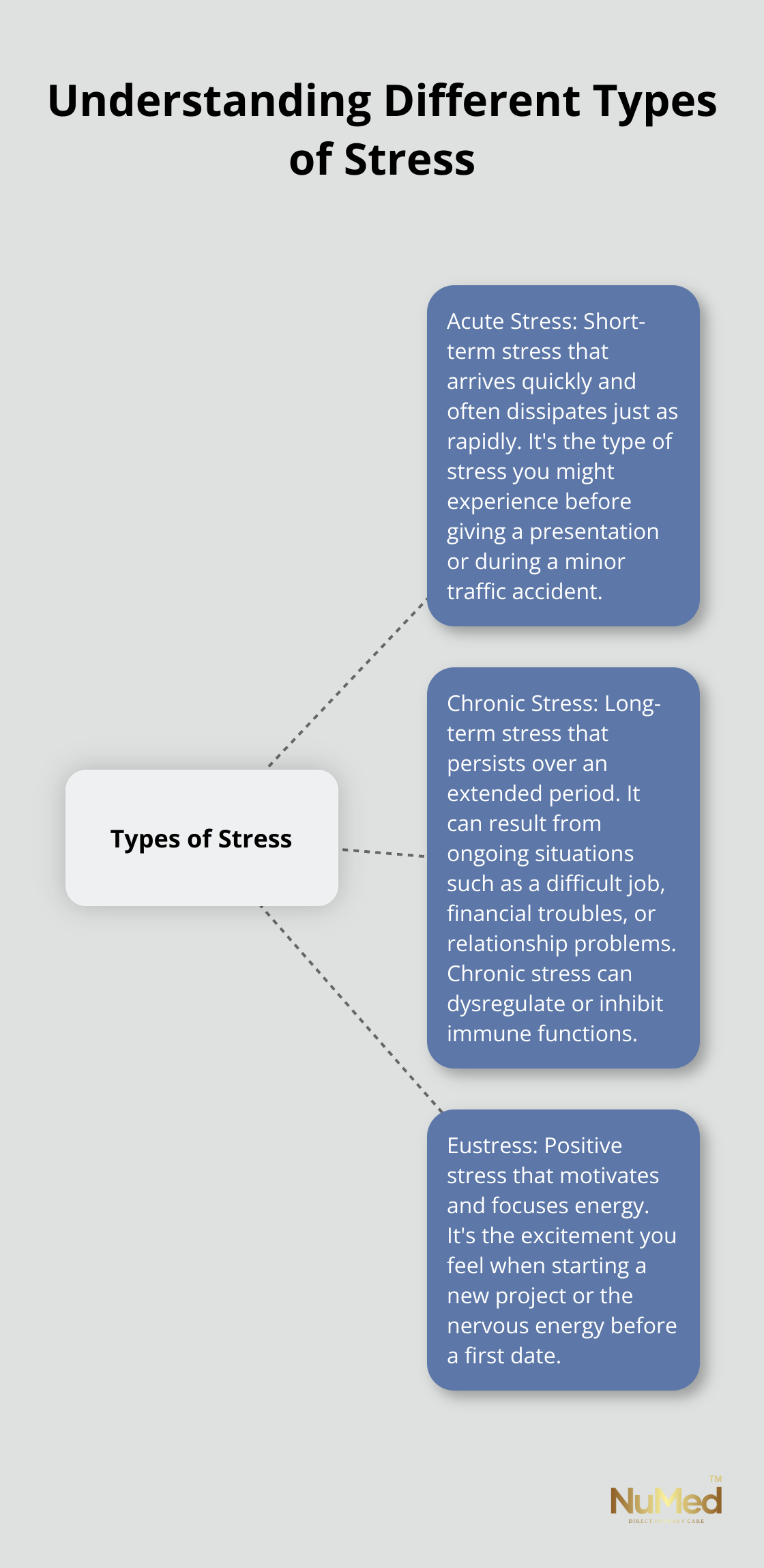
Different Types of Stress
Stress manifests in various forms:
- Acute stress: This short-term stress arrives quickly and often dissipates just as rapidly. It’s the type of stress you might experience before giving a presentation or during a minor traffic accident.
- Chronic stress: This long-term stress persists over an extended period. It can result from ongoing situations such as a difficult job, financial troubles, or relationship problems. Chronic stress dysregulates or inhibits immune functions.
- Eustress: This positive stress motivates and focuses energy. It’s the excitement you feel when starting a new project or the nervous energy before a first date.
How Our Body Adapts to Stress
Our body possesses remarkable ways to adapt to stress, but these mechanisms can become overwhelmed. The General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) model describes three stages of stress response:
- Alarm: The initial reaction where the body releases stress hormones.
- Resistance: The body attempts to cope with the stressor.
- Exhaustion: If the stress continues, the body’s resources become depleted.
Understanding these stages can help us recognize when we push our limits and need to take action to manage our stress levels.
The Physical Manifestations of Stress
Chronic stress often manifests in various physical symptoms. Patients frequently report unexplained fatigue, frequent headaches, or digestive issues that stem from ongoing stress. Addressing these underlying causes can lead to better overall health outcomes.
As we move forward, we’ll explore how stress impacts our physical health in more detail, examining its effects on various bodily systems and functions.
How Stress Harms Your Body
Stress doesn’t just affect your mind; it takes a significant toll on your physical health. Let’s explore how stress impacts different systems in your body and what you can do about it.
Your Heart Under Pressure
Stress puts your heart into overdrive. Your blood pressure rises, and your heart rate increases. This extra strain on your cardiovascular system can have serious consequences. A study found that work-related stress is associated with unfavorable cardiovascular health.
To protect your heart, incorporate stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine. A 10-minute walk can lower your blood pressure and reduce stress hormones.
Digestive Distress and Metabolic Mayhem
Stress disrupts your digestive system. It can cause acid reflux, stomach ulcers, and changes in your gut microbiome. Many people report worsening symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) during stressful periods.
Stress also affects your metabolism. It can increase your appetite, especially for high-calorie comfort foods. This often leads to weight gain, which in turn can cause more stress (creating a vicious cycle).
To combat these effects, maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Practice mindful eating to reduce stress-induced overeating.
Your Immune System Takes a Hit
Chronic stress suppresses your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Research shows that chronic stress can increase the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10, further dampening the immune response.
To boost your immune system, prioritize sleep, exercise regularly, and consider stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga. These practices can help balance your stress hormones and strengthen your body’s defenses.
The Sleep-Stress Connection
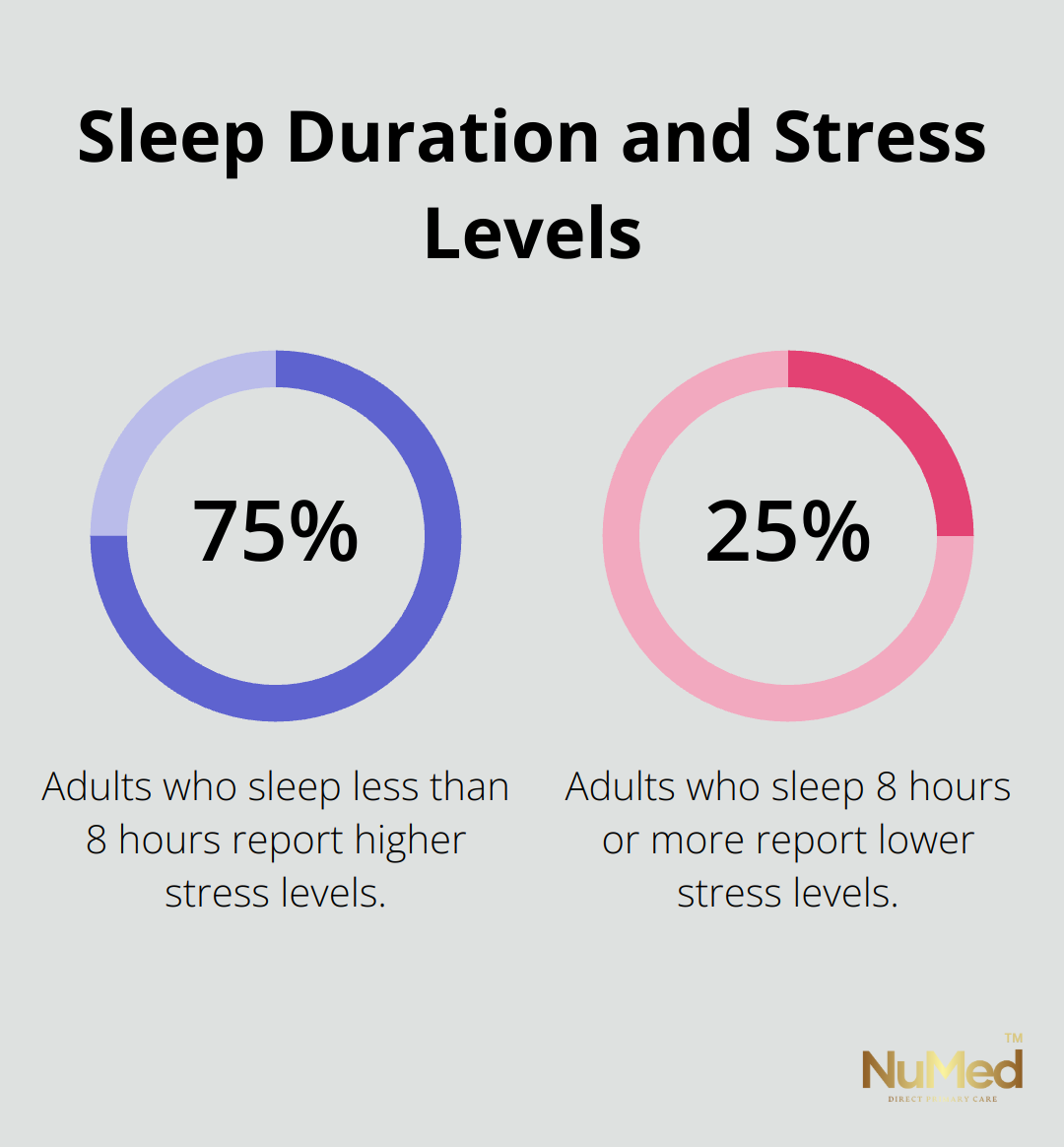
Stress often leads to sleep disturbances, creating a cycle of fatigue and increased stress. The American Psychological Association reports that adults who sleep fewer than eight hours a night report higher stress levels compared to those who sleep more.
To improve your sleep, establish a consistent bedtime routine, limit screen time before bed, and create a calm sleep environment. If sleep problems persist, don’t hesitate to seek professional help.
As we’ve seen, stress can significantly impact various bodily systems. But the effects of stress don’t stop at physical health. In the next section, we’ll examine how stress influences our psychological and emotional well-being, and explore strategies to maintain mental balance in the face of life’s challenges.
How Stress Impacts Your Mind
The Anxiety-Stress Connection
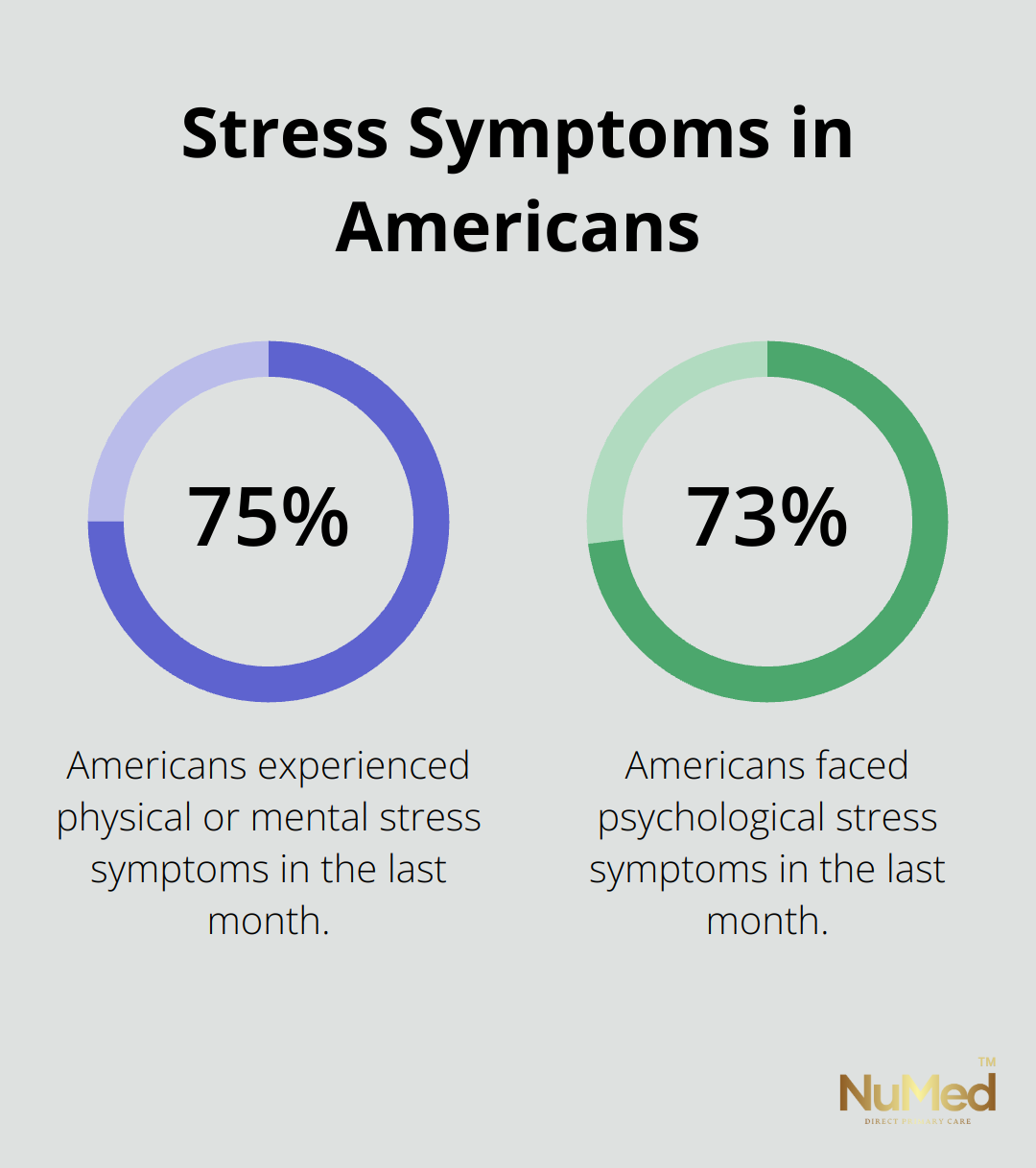
Stress and anxiety often intertwine. Around 75% of Americans reported to the American Psychological Association that they experienced a physical or mental symptom of stress in the last month, while 73% face psychological symptoms. These symptoms can manifest as persistent worry, restlessness, and difficulty relaxing.
To combat stress-induced anxiety, incorporate mindfulness practices into your daily routine. Research shows that mindfulness, particularly through Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR), improves emotional regulation and brain structure, reduces anxiety, and enhances stress management.
Stress and Cognitive Function
Chronic stress impairs cognitive abilities, affecting memory, concentration, and decision-making skills. Research from the University of California, Irvine, shows that even short-term stress impacts the brain’s ability to create and store new memories.
To protect your cognitive function, prioritize stress-reduction activities. Regular exercise not only reduces stress but also boosts cognitive performance. A study in the British Journal of Sports Medicine found that even a single bout of moderate exercise enhances memory and cognitive processing.
The Emotional Rollercoaster
Stress leads to mood swings and irritability, making it challenging to maintain stable relationships and perform well at work. The National Institute of Mental Health notes that chronic stress contributes to the development of mood disorders like depression.
To stabilize your mood, maintain a balanced lifestyle. This includes regular sleep patterns, a healthy diet, and consistent exercise. Additionally, social connections play a crucial role in emotional regulation. A study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that strong social relationships buffer the effects of stress on mental health.
Stress Management Techniques
Effective stress management is key to maintaining mental well-being. Try these techniques:
- Deep breathing exercises (they can lower heart rate and blood pressure)
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Guided imagery
- Regular physical activity (aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week)
- Journaling or expressive writing
Seeking Professional Help
If stress significantly impacts your daily life, consider seeking professional help. Mental health professionals can provide tailored strategies to manage stress and improve overall well-being. They may recommend cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness-based stress reduction, or other evidence-based approaches to help you cope with stress more effectively.
Final Thoughts
The principle of stress impacts our lives profoundly, affecting physical health and mental well-being. From cardiovascular strain to cognitive impairments, stress has far-reaching effects that highlight the need for effective management strategies. We at NuMed Direct Primary Care understand the complex interplay between stress and health, focusing on addressing root causes to prevent illness and promote overall well-being.
Stress management requires patience, persistence, and sometimes professional guidance. Our approach offers personalized care that considers your unique circumstances and health goals (helping you develop effective strategies to manage stress). We provide support and tools to navigate life’s challenges more effectively, leading to improved physical and emotional health.
If stress significantly impacts your daily life, don’t hesitate to reach out for help. NuMed Direct Primary Care can assist you in taking a crucial step towards a healthier, more balanced life. Your future self will appreciate the effort you invest today in understanding and addressing the principle of stress.
















