Traditional medicine treats everyone the same way, but your DNA tells a different story. The benefits of personalized medicine are transforming how we approach healthcare by tailoring treatments to your unique genetic makeup.
We at NuMed DPC see firsthand how precision medicine improves patient outcomes. This targeted approach reduces side effects while maximizing treatment effectiveness for each individual patient.
How Does Personalized Medicine Actually Work
Personalized medicine analyzes your genetic code to determine which treatments work best for your body. Genetic variations can optimize treatment outcomes when therapies match your specific DNA profile, particularly in determining appropriate drug dosages based on individual genetic makeup. This approach to medical treatment examines over 15,000 genetic tests available for more than 2,800 genes, which identify disease risks before symptoms appear. Genetic tests reveal how your body metabolizes medications, which prevents the trial-and-error approach that affects half of all patients who don’t benefit from their initial prescriptions.
Genetic Tests Transform Treatment Decisions
Your genetic profile determines medication effectiveness and dosage requirements. The FDA recommends genetic tests before doctors prescribe warfarin to prevent serious adverse reactions. Tests like Oncotype DX predict breast cancer recurrence and guide chemotherapy decisions, while pharmacogenomic tests identify optimal psychiatric medications based on your genetic makeup. These biomarkers eliminate guesswork in treatment selection, which reduces the hospital admissions caused by adverse drug reactions, which account for 10-20% of all hospital admissions.
Traditional Medicine Misses Individual Differences
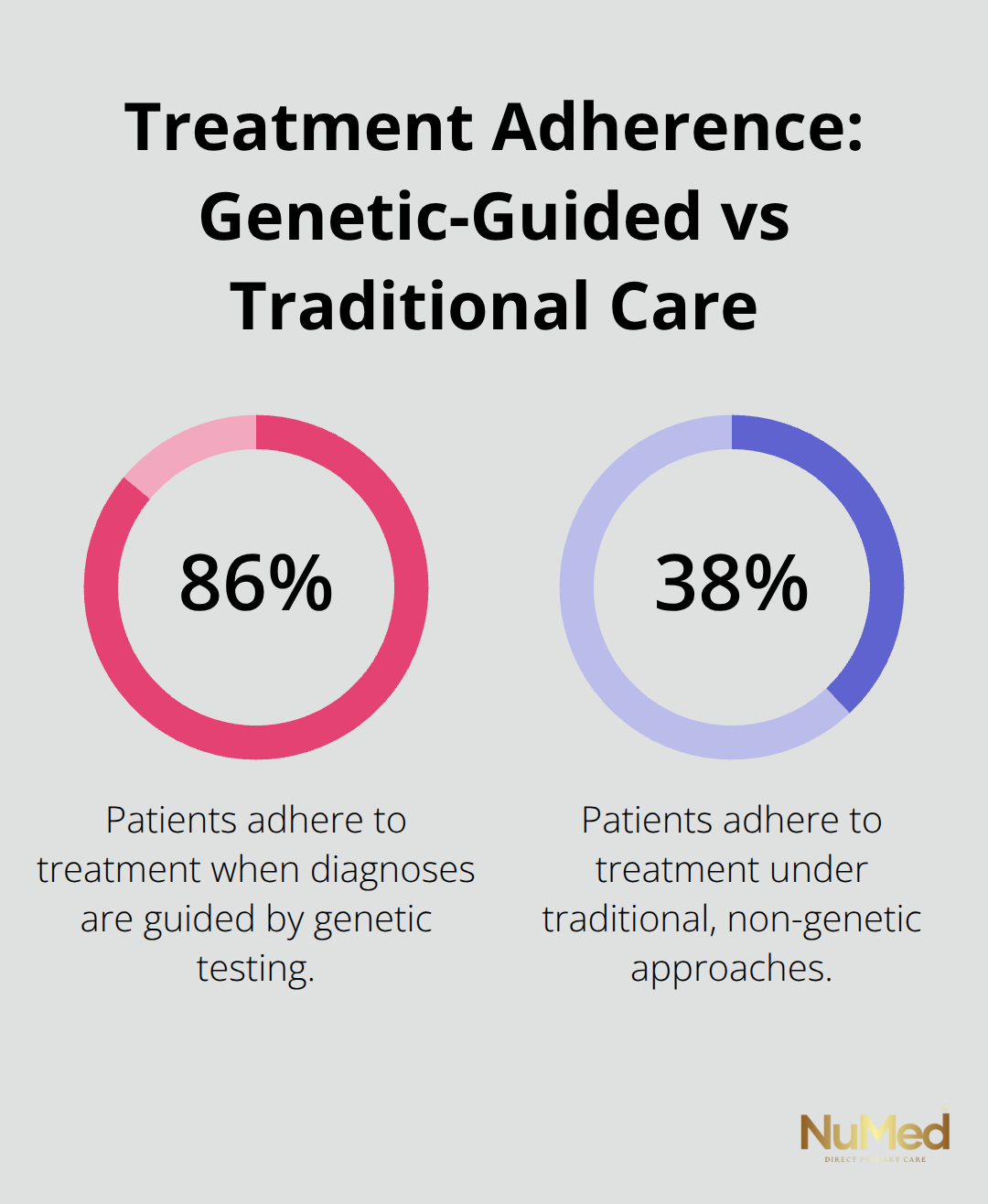
Standard healthcare protocols treat all patients identically and ignore genetic variations that affect treatment outcomes. Traditional approaches rely on population averages rather than individual characteristics, which leads to ineffective treatments and unnecessary side effects. Personalized medicine replaces this one-size-fits-all model with targeted interventions based on your unique biological markers. Studies show 86% treatment adherence in patients who receive genetic-based diagnoses compared to 38% with traditional approaches (particularly in chronic disease management).
Biomarkers Guide Precision Treatment Plans
Doctors use specific biomarkers to select the most effective therapies from the start. Molecular tests identify which cancer patients will respond to targeted drugs like Iressa, which transforms treatment from reactive to proactive care. These precision tools help physicians avoid medications that won’t work for your genetic profile, which saves time and reduces harmful side effects. The shift toward biomarker-guided treatment represents a fundamental change in how medicine approaches individual patient care, setting the stage for even more targeted therapeutic advances.
Why Personalized Medicine Works Better
Treatment Success Rates Double With Genetic Guidance
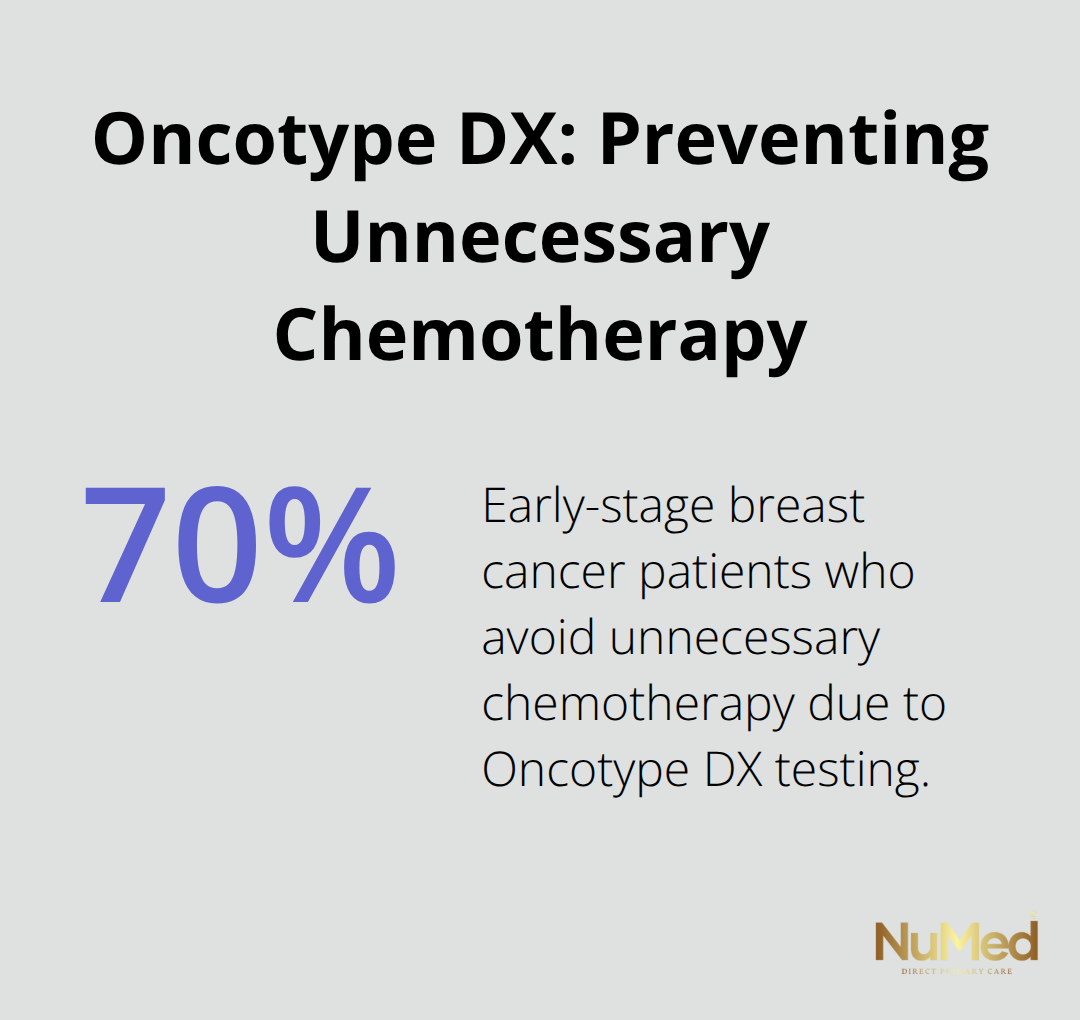
Personalized medicine dramatically improves treatment outcomes when doctors match therapies to your genetic profile. Cancer patients who receive targeted treatments based on genetic markers show significantly better survival rates compared to standard chemotherapy protocols. The National Institutes of Health reports that personalized medicine improves drug response rates when physicians identify genetic variations that affect medication effectiveness. Oncotype DX testing prevents unnecessary chemotherapy in 70% of early-stage breast cancer patients while it identifies those who truly need aggressive treatment. These genetic insights transform medicine from guesswork into precision targeting.
Genetic Tests Prevent Dangerous Drug Reactions
Up to 50% of patients experience no benefit from their initial prescriptions due to genetic differences in drug metabolism. Pharmacogenomic tests eliminate this trial-and-error approach that causes adverse drug reactions responsible for 3-10% of hospital admissions, according to clinical studies. The TMPT test prevents toxic side effects in children with leukemia when doctors determine correct medication dosages based on genetic markers. Warfarin genetic tests reduce bleeding complications by 30% when physicians adjust doses according to patient DNA profiles. These preventive measures save lives while they reduce healthcare costs through fewer emergency interventions.
Early Detection Transforms Disease Prevention
Genetic tests reveal disease predispositions decades before symptoms appear, which enables proactive prevention strategies. BRCA gene tests identify breast and ovarian cancer risks, which prompt increased screening and prophylactic surgeries that reduce cancer deaths by 90%. Hereditary heart disease markers allow cardiologists to implement targeted lifestyle interventions and medications before cardiovascular events occur. The American Society of Clinical Oncology emphasizes that early genetic detection provides treatment options when diseases are most manageable, rather than when physicians wait for advanced stages where intervention becomes limited.
Precision Medicine Reduces Healthcare Costs
Targeted treatments eliminate expensive trial-and-error approaches that burden both patients and healthcare systems. Studies demonstrate that personalized medicine reduces unnecessary testing and improves resource allocation (particularly in oncology, where genetic markers guide treatment selection). Patients who receive genetic-based diagnoses show 86% treatment adherence compared to 38% with traditional approaches, which reduces costly complications and repeat hospitalizations. These success stories in precision medicine set the foundation for understanding how specific medical conditions benefit from personalized approaches across different specialties.
How Does Precision Medicine Work in Practice
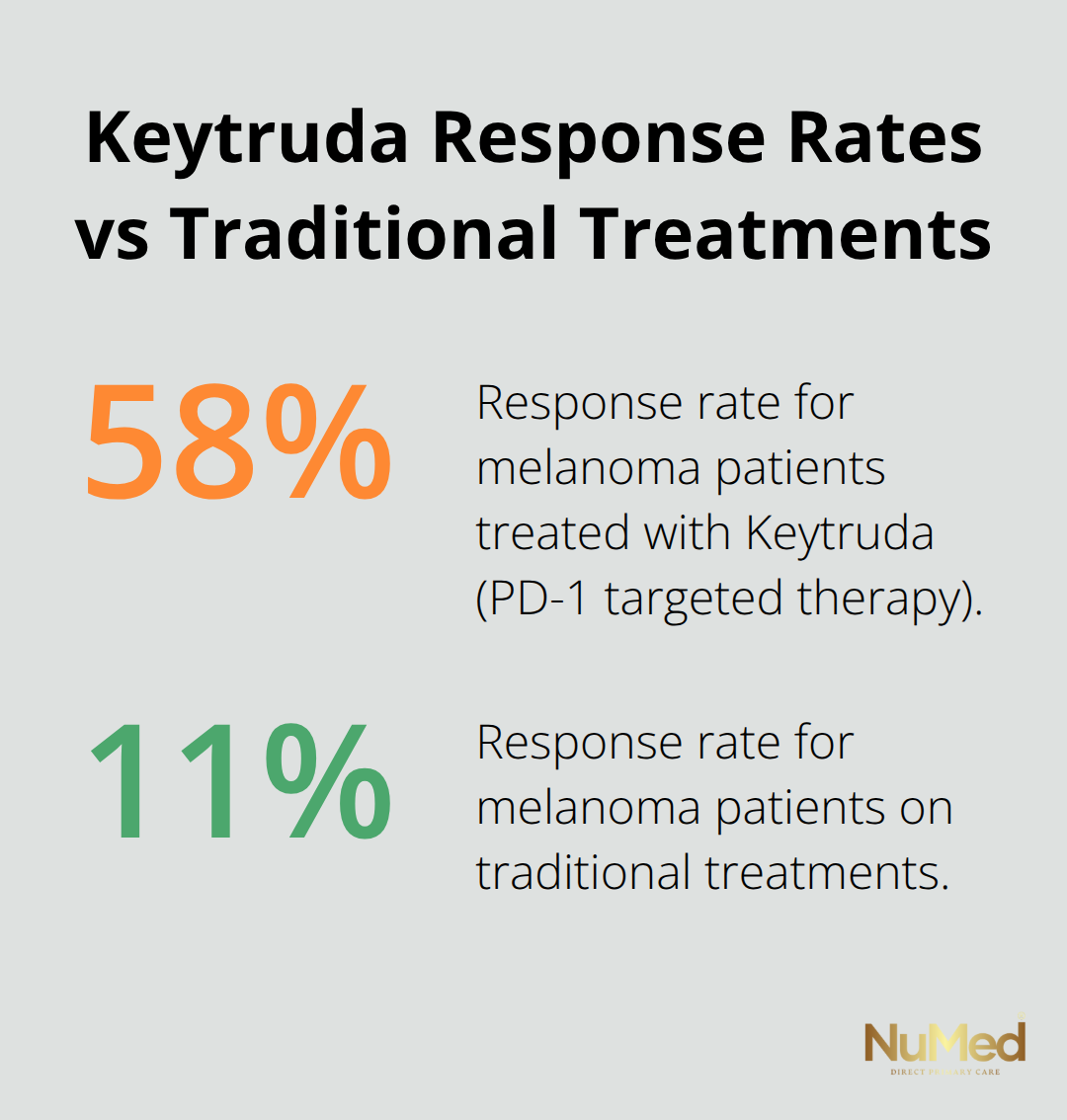
Cancer treatment transformed when doctors started to match therapies to tumor genetics rather than treat all cancers the same way. The FDA approved over 200 targeted cancer drugs that work specifically for patients with certain genetic mutations. Herceptin treats breast cancers with HER2 protein overexpression and improves survival rates by 40% compared to standard chemotherapy. Keytruda targets PD-1 proteins in melanoma patients and achieves response rates of 58% versus 11% with traditional treatments. Genetic tests like Foundation One CDx analyze 324 cancer-related genes to identify which targeted therapies will work best for each patient’s specific tumor profile.
Mental Health Medications Match Your Genetic Code
Psychiatric medications cause severe side effects in 30% of patients due to genetic variations in drug metabolism. GeneSight tests analyze how your liver processes antidepressants, antipsychotics, and mood stabilizers before doctors prescribe them. Patients with specific CYP2D6 gene variants metabolize medications like Prozac and Risperdal differently and require dose adjustments to prevent toxicity or treatment failure. The Mayo Clinic reports that pharmacogenomic tests reduce psychiatric medication trials from an average of 4.2 attempts to 1.8 attempts.
Heart Disease Prevention Through Genetic Guidance
Heart disease patients benefit when genetic tests guide warfarin dose selection and prevent dangerous complications that occur in 15% of patients on standard protocols. Genetic variations in the VKORC1 and CYP2C9 genes determine how quickly patients metabolize blood thinners. Doctors who use genetic test results implement clinical pharmacogenomic testing protocols that improve patient outcomes through personalized medication management. Statin medications also work differently based on genetic markers, with some patients requiring alternative cholesterol drugs to avoid muscle damage.
Diabetes and Asthma Respond to Genetic Insights
Type 2 diabetes patients with specific genetic markers respond better to metformin versus sulfonylureas, while others require insulin therapy from diagnosis. Genetic tests identify MODY diabetes in patients misdiagnosed with Type 1 diabetes and allow them to switch from insulin injections to oral medications. Asthma patients with beta-2 receptor genetic variants show poor response to albuterol inhalers but respond well to alternative bronchodilators. The American Diabetes Association now recommends genetic tests for young-onset diabetes to guide treatment selection. These precision approaches increase treatment adherence to 86% compared to 38% with standard care protocols and work similarly to personalized nutrition plans that use advanced testing to optimize individual health outcomes.
Final Thoughts
The benefits of personalized medicine represent a fundamental shift from reactive to proactive healthcare. Genetic tests reduce adverse drug reactions by 30%, improve treatment adherence to 86%, and enable early disease detection decades before symptoms appear. Cancer patients who receive targeted therapies show dramatically better survival rates, while pharmacogenomic tests eliminate dangerous trial-and-error prescriptions that affect half of all patients.
Direct primary care models like NuMed DPC support personalized treatment through extensive lab services and functional medicine approaches that address root causes rather than symptoms. This model allows physicians to spend adequate time when they analyze genetic profiles and implement precision treatment plans without insurance restrictions. Patients receive comprehensive care that focuses on their individual biological markers and health needs.
The future of precision healthcare will expand genetic test accessibility and integrate AI-driven analysis for even more targeted interventions. Costs decrease and technology advances, which make personalized medicine standard care rather than specialized treatment (replacing the current one-size-fits-all approach). Patients who embrace genetic-guided healthcare today position themselves for better health outcomes and reduced medical complications throughout their lives.