Anxiety disorders affect 40 million adults in the United States annually, yet traditional treatments don’t work for everyone. Standard medications can take weeks to show results and often come with unwanted side effects.
Ketamine therapy for anxiety represents a breakthrough approach that works differently from conventional antidepressants. We at NuMed DPC have seen this innovative treatment offer hope for patients who haven’t found relief through traditional methods.
How Does Ketamine Work Differently for Anxiety
Unique Mechanism of Action
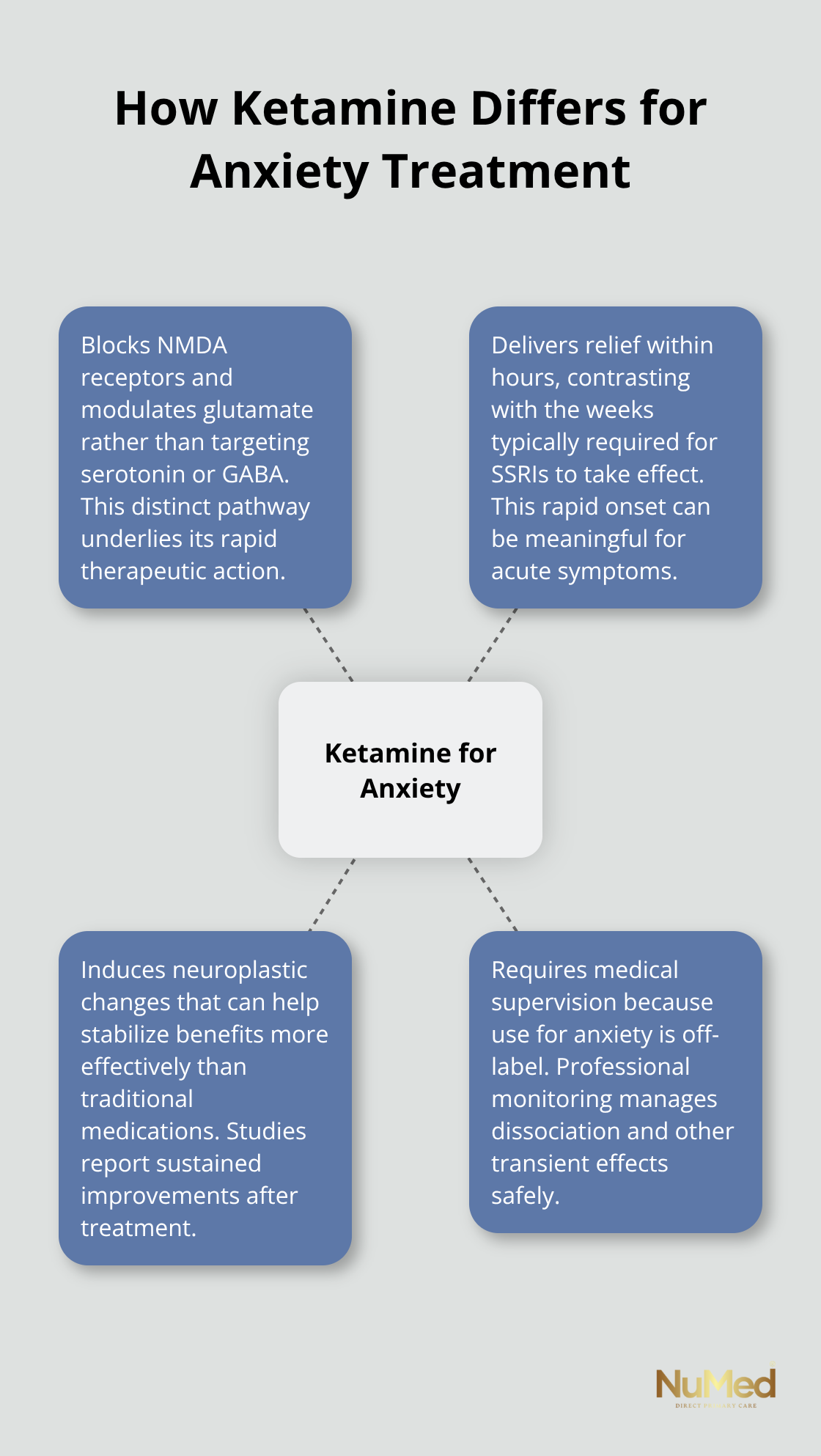
Ketamine operates through a fundamentally different mechanism than traditional anxiety medications. Instead of targeting serotonin or GABA receptors like conventional treatments, ketamine blocks NMDA receptors in the brain and affects glutamate levels. This action enhances synaptic plasticity and produces rapid anxiety relief within hours rather than the weeks that SSRIs typically require to take effect. Research demonstrates that patients with generalized anxiety disorder can experience rapid and lasting reductions in anxiety symptoms after ketamine treatments, with effects that may persist for days after a single session.
Traditional Medications vs Ketamine Treatment
Standard anxiety medications work by gradually increasing neurotransmitter availability over weeks or months. Ketamine therapy produces immediate neuroplastic changes that allow therapeutic benefits to stabilize more effectively than traditional treatments. Clinical studies indicate that ketamine intravenous therapy can significantly reduce anxiety symptoms compared to traditional medications, with sustained improvement over extended periods. The effectiveness in treating patients with treatment-resistant cases demonstrates ketamine’s potential for situations where conventional therapies have failed.
Medical Supervision Requirements
Ketamine remains off-label for anxiety treatment, as the FDA has not yet approved it for any psychiatric disorders beyond esketamine for treatment-resistant depression (approved in 2019). This means ketamine therapy requires careful medical supervision in controlled clinical settings. The American Society of Ketamine Physicians recommends that patients evaluate clinics based on their mental health service offerings and staff qualifications. Safety screenings and monitoring during treatment are essential, as side effects can include dissociation, transient hallucinations, and cognitive effects that require professional oversight.
These unique properties and requirements make ketamine therapy distinct from conventional approaches, but understanding the clinical evidence behind these claims provides the complete picture of its effectiveness.
What Does Research Say About Ketamine for Anxiety
Recent Clinical Trial Results
The KARMA-Dep 2 trial conducted at Trinity College Dublin provides the most comprehensive real-world evidence for ketamine therapy. This study involved 65 participants and compared ketamine infusions to midazolam (an active placebo). The results showed that 47% of ketamine patients achieved remission compared to 30% who received midazolam. However, the mean difference on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale was only 3.16 points, which fell short of clinical significance.
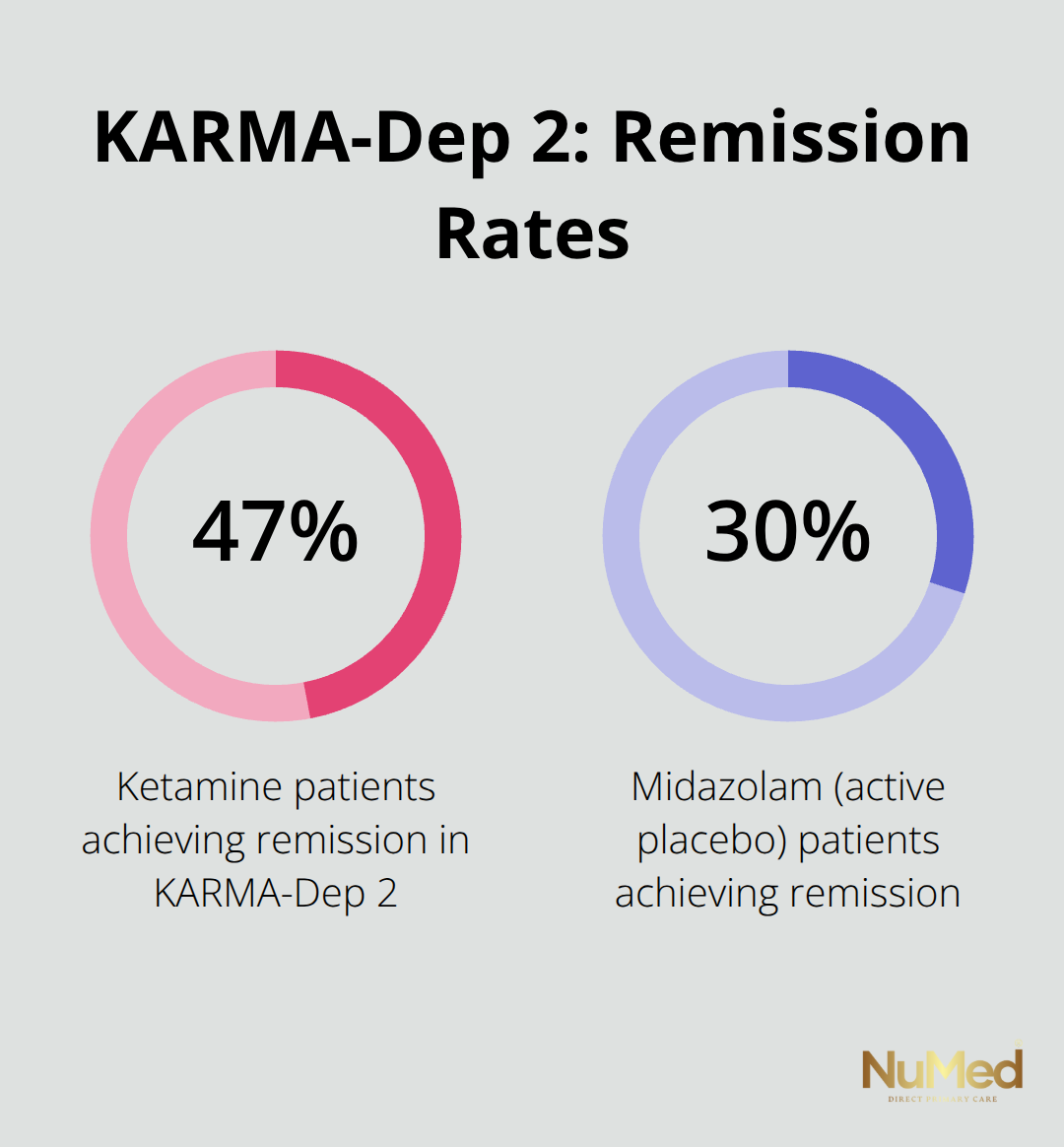
Both groups maintained similar relapse rates during six-month follow-up periods, which indicates that ketamine’s superiority may be less pronounced than researchers initially believed.
Success Rates Across Different Conditions
Studies demonstrate that ketamine shows promising results in treating various anxiety-related conditions, though specific success rates vary across different patient populations. For substance-related anxiety, randomized clinical trials found that 66% of participants maintained abstinence after ketamine treatment. A 2023 analysis revealed that ketamine intravenous therapy significantly reduced anxiety symptoms compared to traditional medications, with sustained improvement that lasted over one year. However, recent research shows significant reductions in depression scores by day 3 compared to placebo groups, indicating ketamine’s rapid therapeutic potential.
Placebo Effect Considerations
The effectiveness becomes more questionable when studies use psychoactive placebos rather than inert saline solutions. Meta-analyses show larger effect sizes when researchers compare ketamine to inert saline rather than psychoactive placebos, which potentially exaggerates perceived benefits. A significant finding from the KARMA-Dep 2 trial was that 90% of raters could identify who received ketamine treatment after the first infusion, which raises concerns about treatment bias and suggests that initial optimism may have been overstated.
Treatment Response Timeline
Ketamine produces rapid onset effects within hours, which contrasts sharply with traditional anxiolytics that require weeks for therapeutic benefits. The drug’s clearance rate of approximately 95 L/h/70kg contributes to its short duration of action, with effects that potentially last up to seven days after a single treatment session. Clinical studies show that repeated infusions may not provide significant advantages over single treatments, which challenges assumptions about optimal treatment protocols and raises important questions about the practical aspects of ketamine therapy administration.
What Happens During Ketamine Treatment
Treatment Session Protocol
Ketamine therapy sessions last 2-3 hours in a controlled medical environment. Medical professionals administer ketamine through intravenous infusions, which provide rapid absorption. Patients remain under continuous medical supervision throughout the session, as dissociative effects begin within minutes of administration.
The actual infusion period lasts 40-60 minutes, followed by a recovery phase where patients may experience vivid dreams, mild hallucinations, or disorientation. Medical staff monitor vital signs continuously and provide immediate support if adverse reactions occur. Most patients can return home the same day, though doctors restrict patients from driving for 24 hours post-treatment.
Common Side Effects and Reactions
Patients frequently experience fatigue, sleep disturbances, confusion, drowsiness, and dizziness during the recovery phase. Studies have found mild liver enzyme elevations in some patients, though no serious adverse events proved fatal. These effects typically resolve within hours after treatment completion.
Dissociative symptoms represent the most notable aspect of ketamine therapy. Patients report feelings of detachment from their body or surroundings during the infusion period. These sensations usually subside as the medication clears from the system.
Safety Precautions and Contraindications
Patients must avoid alcohol consumption before and after treatment due to the increased risk of respiratory depression. Ketamine should never be combined with other CNS depressants without medical approval. Healthcare providers conduct thorough screenings to identify potential contraindications before treatment begins.
Serious complications remain rare when administered in proper clinical settings, but emergency protocols must be available. Medical facilities require specialized equipment and trained staff to handle potential adverse reactions safely.
Treatment Costs and Insurance Coverage
Treatment costs range from $400-800 per session, with most insurance plans not covering off-label ketamine therapy for anxiety. Patients typically require 6-8 sessions over several weeks, creating total treatment costs between $2,400-6,400 before potential insurance reimbursement. Some clinics offer payment plans or package deals to help manage these expenses.

Final Thoughts
Ketamine therapy for anxiety shows promise but requires careful consideration of the evidence. The KARMA-Dep 2 trial revealed that while 47% of patients achieved remission, the clinical significance remained limited compared to active placebos. Success rates vary significantly across different conditions, with some studies showing 66% abstinence rates for substance-related anxiety.
The rapid onset within hours distinguishes ketamine from traditional treatments that take weeks to work. However, costs range from $2,400-6,400 for complete treatment courses, and limited insurance coverage creates accessibility barriers. Ideal candidates include patients with treatment-resistant anxiety who haven’t responded to conventional medications and can afford the financial investment.
Medical supervision remains essential given the off-label status and potential side effects (including dissociation and cognitive changes). We at NuMed DPC understand the importance of comprehensive healthcare approaches that address root causes while providing personalized care. The decision to pursue ketamine therapy for anxiety should involve a thorough evaluation of individual circumstances, treatment history, and realistic expectations about outcomes.
















